Sunday, September 29, 2013
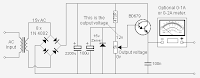
HANDY 0 12V DC POWER SUPPLY ELECTRONIC DIAGRAM
For heat protection, heat sink is needed for the BD679 transistor. It is because it will be over tempered when works more than 200mA.
FEATURES:
0v to 12 volt output:
- 700mA with M 2155
- 1.4amp with M 2156
- 1A with 16v AC 1.5 amp plug pack
Friday, September 27, 2013
Push Button Relay Selector
Gate IC1a is connected as a relax-ation oscillator which runs at about 20kHz. Pulses from the oscillator are fed to IC1b, where they are gated with a control signal from IC1c. The result is inverted by IC1d and fed into the clock input (CP0) of IC2. Initially, we assume that the reset switch (S1) has been pressed, which forces a logic high at the O0 output (pin 3) of IC2 and logic lows at all other outputs (O1-O9). As the relay driver transistors (Q1-Q4) are switched by these outputs, none of the relays will be energised after a reset and none of the load devices (speakers, etc) will be selected. Now consider what happens if you press one of the selector switches (S2-S5, etc). For example, pressing S5 connects the O4 output (pin 10) of IC2 to the input (pin 9) of IC1c, pulling it low.
 This causes the output (pin 10) to go high, which in turn pulls the input of IC1b (pin 5) high and allows clock pulses to pass through to decade counter IC2. The 4017B counts up until a high level appears at its O4 output. This high signal is fed via S5 to pin 9 of NAND gate IC1c, which causes its output (pin 10) to go low. This low signal also appears on pin 5 of IC1b, which is then inhibited from passing further clock pulses on its other input (pin 6) through to its output (pin 4), thus halting the counter. So, the counter runs just long enough to make the output connected to the switch that is pressed go high. This sequence repeats regardless of which selector switch you press, so the circuit functions as an electronic interlock system.
This causes the output (pin 10) to go high, which in turn pulls the input of IC1b (pin 5) high and allows clock pulses to pass through to decade counter IC2. The 4017B counts up until a high level appears at its O4 output. This high signal is fed via S5 to pin 9 of NAND gate IC1c, which causes its output (pin 10) to go low. This low signal also appears on pin 5 of IC1b, which is then inhibited from passing further clock pulses on its other input (pin 6) through to its output (pin 4), thus halting the counter. So, the counter runs just long enough to make the output connected to the switch that is pressed go high. This sequence repeats regardless of which selector switch you press, so the circuit functions as an electronic interlock system.Each relay driver circuit is a 2N7000 FET switch with its gate driven from one output of IC2 via a 100W resistor. The relay coil is connected from the drain to the +12V supply rail, with a reverse diode spike suppressor across each coil. If you want visual indication of the selected output, an optional indicator LED and series resistor can be connected across each relay coil, as shown. For selecting pairs of stereo speakers, we’d suggest the use of relays like the Jaycar SY-4052. These operate from 12V and have DPDT contacts rated for 5A. Note that although four selector switches are shown in the circuit, only two relay drivers are shown because of limited space. For a 4-way selector, identical relay drivers would be driven from the O2 and O3 outputs of IC2.
Wednesday, September 25, 2013
A Bedside Lamp Timer Circuit
30 minutes operation, Blinking LED signals 6 last minutes before turn-off
The purpose of this circuit is to power a lamp or other appliance for a given time (30 minutes in this case), and then to turn it off. It is useful when reading at bed by night, turning off the bedside lamp automatically in case the reader falls asleep... After turn-on by P1 pushbutton, the LED illuminates for around 25 minutes, but then it starts to blink for two minutes, stops blinking for two minutes and blinks for another two just before switching the lamp off, thus signaling that the on-time is ending. If the user want to prolong the reading, he/she can earn another half-hour of light by pushing on P1. Turning-off the lamp at users ease is obtained by pushing on P2.
Circuit diagram:
 A Bedside Lamp Timer Circuit Diagram
A Bedside Lamp Timer Circuit Diagram
Parts:
Resistors
R1 = 1K
R2 = 4K7
R3 = 10M
R4 = 1M
R5 = 10K
Capacitors
C1 = 470µF-25V
C2-C4100nF-63V
Semiconductors
C1 = 470µF-25V
C2-C4 = 100nF-63V
D1-D4 = 1N4002
D5 = 5mm. Red LED
IC1 = CD4012
IC2 = CD4060
Q1 = BC328
Q2 = BC547
Miscellaneous
P1,P2 = SPST Pushbuttons
T1 = 9+9 Volt Secondary 1VA Mains transformer
RL1 = 10.5V 470 Ohm Relay with SPDT 2A 220V switch
PL1 = Male Mains plug
SK1 = Female Mains socket
Circuit operation:
Q1 and Q2 form an ALL-ON ALL-OFF circuit that in the off state draws no significant current. P1 starts the circuit, the relay is turned on and the two ICs are powered. The lamp is powered by the relay switch, and IC2 is reset with a positive voltage at pin 12. IC2 starts oscillating at a frequency set by R4 and C4. With the values shown, pin 3 goes high after around 30 minutes, turning off the circuit via C3. During the c6 minutes preceding turn-off.
The LED does a blinking action by connections of IC1 to pins 1, 2 & 15 of IC2. Blinking frequency is provided by IC2 oscillator at pin 9. The two gates of IC1 are wired in parallel to source more current. If required, a piezo sounder can be connected to pins 1 & 14 of IC1. Obviously, timings can be varied changing C4 and/or R4 values.
Source : www.extremecircuits.net
Monday, September 23, 2013
Fuse Box BMW 528I 1982 Diagram
Fuse Box BMW 528I 1982 Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: normal speed relay, high speed relay, low beam check relay, high beam relay, low beam relay, fog light relay, main relay, purge valve relay, fuel pump relay, horn relay, wiper control unit, unloader relay.
Saturday, September 21, 2013
Roper 2079b00 Wiring Diagram
 |
| Roper 2079b00 Wiring Diagram |
Wednesday, September 11, 2013
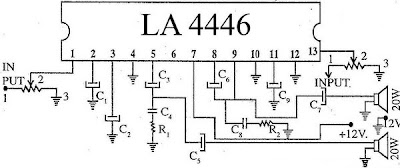
Top Performance LA4446 Stereo Audio Amplifier Circuit
- Low pop noise at power ON/OFF time
- Good ripple rejection: 46dB(typ)
- Good channel separation
- Low residual noise (Rg=0)
- On chip protectors as Thermal protector, Over-voltage/Surge Protector, and pin short protector
Tuesday, September 3, 2013
Mini Drill Speed Regulator Using Voltage Regulator
Mini Drill Speed Regulator Circuit diagram
With the P2 potentiometer can be adjusted the degree of coupling (coupling the output voltage increases with increasing output current). Thus remains constant preset speed. Maximum voltage measured when the P2 is turned up must be about 20% lower than the maximum allowable voltage of the motor (if is not, the value of R1 should be reduced or enlarged accordingly). Voltage regulator is designed with thermal protection, but it must be mounted on a properly dimensioned radiator.
Sunday, September 1, 2013
FM Beacon Broadcast Transmitter 88 108 MHz
Fine frequency adjustment can be made by adjusting the 200 ohm resistor in series with the battery. Oscillator frequency is set by a 5 turn tapped inductor and 13 pF capacitor. The inductor was wound around a #8 X 32 bolt (about 3/16 diameter) and then removed by unscrewing the bolt. The inductor was then streached to about a 3/8 inch length and tapped near the center.
FM Beacon Broadcast Transmitter Circuit Diagram
The oscillator frequency should come out somewhere near the center of the band (98 MHz) and can be shifted higher or lower by slightly expanding or compressing the inductor. A small signal diode (1N914 or 1N4148) is used as a varactor diode so that the total capacity in parallel with the inductor varies slightly at the audio rate thus causing the oscillator frequency to change at the audio rate (600 Hz).
The ramping waveform at pins 2 and 6 of the timer is applied to the reversed biased diode through a large (1 Meg) resistor so that the capacitance of the diode changes as the ramping voltage changes thus altering the frequency of the tank circuit. Alternately, an audio signal could be applied to the 1 Meg resistor to modulate the oscillator but it may require an additional pullup resistor to reverse bias the diode. The N channel JFET transistors used should be high frequency VHF or UHF types (Radio Shack #276-2062 MPF102) or similar.